What is HS Code (Harmonized System Code)?
The HS Code, or Harmonized System Code, is a standardized numerical method of classifying traded products. Developed and maintained by the World Customs Organization (WCO), this system is essential for international trade, providing a common language for goods classification. It consists of a six-digit code that helps identify products universally, though countries may add additional digits for national classification purposes.
Why Are HS Codes Essential in International Trade?
HS Codes serve as the backbone of global trade, acting as a universal classification system for goods that simplifies and streamlines international shipping and customs processes. Their widespread adoption ensures accurate communication between exporters, importers, and customs authorities, minimizing errors and delays.
Smooth Customs Procedures
Using the correct HS Code is crucial for avoiding potential issues at customs. Incorrect codes may be seen as non-compliance or misdeclaration, resulting in penalties, fines, or even shipment rejection. Moreover, inaccurate codes can lead to improper tariff applications, significantly increasing costs for businesses and their customers. Since interpretations of HS Codes can vary across countries, ensuring accuracy is key.
Reliable Trade Data Analysis
The standardization provided by HS Codes enables governments, private organizations, and international institutions to effectively monitor and analyze trade flows. HS Codes play a vital role in:
- Compiling trade statistics.
- Setting internal tax rates.
- Determining rules of origin.
- Shaping trade policies and agreements.
- Tracking transport and freight logistics.
- Managing quotas and price fluctuations.
- Conducting economic research and reporting.
Facilitating Digital Trade Communication
HS Codes are heavily utilized in electronic data exchange systems, such as the United Nations’ Electronic Data Interchange for Administration, Commerce, and Transport (UN/EDIFACT). This integration has made the classification system a global standard for identifying goods, allowing customs and port authorities worldwide to process shipments efficiently.
What Does the HS Code Mean?
Each HS Code consists of sections, chapters, headings, and subheadings:
- Sections: Broad categories of goods, such as machinery or food products.
- Chapters: Specific industries or product types within those sections.
- Headings: Subdivisions within chapters to narrow down the classification further.
- Subheadings: Detailed descriptions of products within headings.
For example:
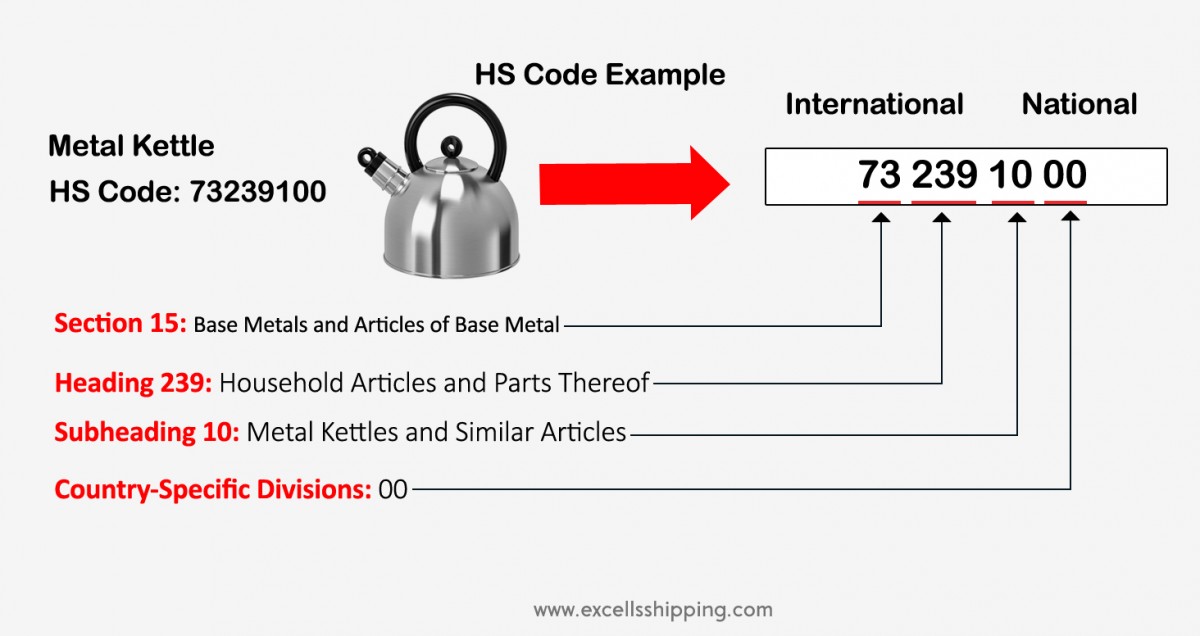
HS Code Example: Metal Kettle
HS Code: 73239100
- Section 15: Base Metals and Articles of Base Metal
- Chapter 73: Articles of Iron or Steel
- Heading 239: Household Articles and Parts Thereof
- Subheading 10: Metal Kettles and Similar Articles
- Country-Specific Divisions: 00
International Structure:
- 73: Base Metal Articles (Chapter)
- 239: Household Articles (Heading)
- 10: Kettles (Subheading)
- 00 00: National Divisions
Where Is the HS Code Used?
The HS Code is used in various stages of international shipping and trade:
- Customs Declarations: To ensure that goods are classified correctly for import/export duties.
- Trade Agreements: To apply appropriate tariffs or preferential treatment.
- Statistical Tracking: Governments and organizations use HS Codes to track trade volumes and trends.
- Compliance: Accurate classification ensures compliance with local and international regulations.
How to Choose the Correct HS Code?
Choosing the right HS Code is crucial for smooth shipping operations. Here’s how you can do it:
- Understand Your Product: Analyze the nature, materials, and usage of the product.
- Consult Official Documentation: Use tools like the WCO’s database or your country’s customs website.
- Seek Expert Advice: If unsure, consult a customs broker or freight forwarder.
- Use Classification Tools: Many online tools allow you to search for HS Codes by product description.
- Stay Updated: HS Codes are periodically updated by the WCO to reflect changes in global trade.
Can Shipping Be Done Without an HS Code?
In most cases, no. Shipping without an HS Code can lead to:
- Delays in customs clearance.
- Incorrect tariff application, resulting in higher costs.
- Fines or penalties for non-compliance.
Customs authorities rely on HS Codes to process shipments efficiently. Providing an inaccurate or missing HS Code may cause complications and, in some cases, seizure of goods.
Are HS Codes Different Across Countries?
The first six digits of an HS Code are standardized globally, but countries can add additional digits for further classification. For example:
- United States: Uses a 10-digit code (Harmonized Tariff Schedule or HTS code).
- European Union: Uses an 8-digit Combined Nomenclature (CN) code.
- China: Uses 10-digit HS Codes with specific subcategories.
While the structure remains consistent, always verify the full code with the importing country’s customs authorities.
FAQs About HS Codes
1. What happens if I use the wrong HS Code? Using the wrong HS Code can lead to:
- Overpayment or underpayment of duties.
- Shipment delays.
- Fines or legal consequences.
2. Are HS Codes the same as HTS Codes? HS Codes form the basis of HTS (Harmonized Tariff Schedule) Codes, which include additional digits specific to each country.
3. How often are HS Codes updated? The WCO updates the HS Code system every five years to adapt to changes in global trade and technology.
4. Can I find HS Codes online? Yes, many customs authorities and organizations provide searchable databases for HS Codes.
5. Do I need a separate HS Code for each product? Yes, every unique product or product category requires its own HS Code.